I. The Precision and Rigors of Firearm Magazine Production
Firearm Magazine Production is a complex process that demands high precision and stringent quality control. These magazines are not merely simple ammunition holders but are crucial components designed to ensure the reliable operation of firearms in various conditions. The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, such as durable steel or reinforced polymers, to guarantee the final product’s durability and reliability. Advanced machining techniques are then employed to achieve precision at the micron level, ensuring that every detail is meticulously crafted for smooth feeding and ejection of ammunition. Additionally, the production process involves multiple rounds of testing and validation, including durability tests, functional tests, and environmental stress tests, to ensure that each magazine meets or exceeds design specifications. This rigorous production approach not only assures product quality but also provides users with the confidence that their equipment will perform flawlessly even in the most demanding situations.
II. CNC milling machine
Briefly Intro
CNC milling machines play a crucial role in Firearm Magazine Production due to their ability to provide high precision and consistency. These machines use computer numerical control technology, allowing precise control over every machining step to ensure each magazine component meets strict tolerance standards.
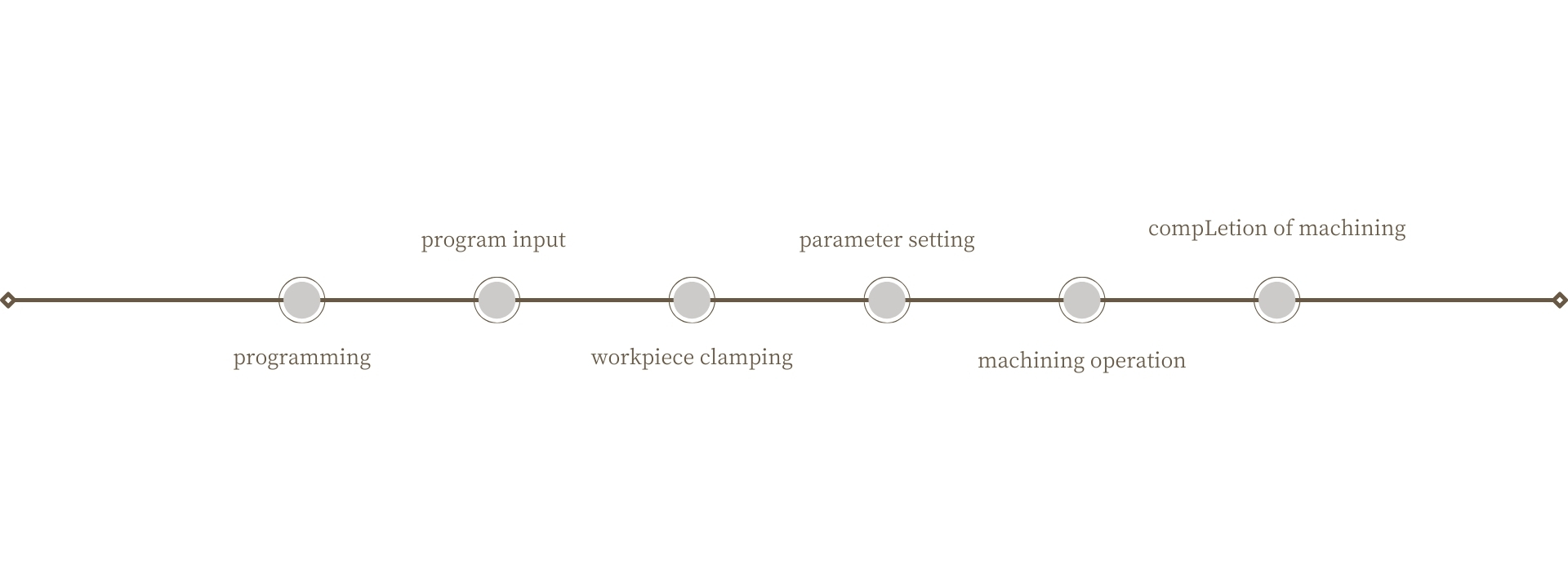
a. Programming
The machining process is programmed based on the CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of the part.
b. Program Input
The completed machining program is input into the CNC control system.
c. Workpiece Clamping
The workpiece to be machined is fixed on the milling machine’s worktable.
d. Parameter Setting
Adjust the cutting speed, feed rate, tool speed, and other parameters of the milling machine according to the parameters set in the machining program.
e. Machining Operation
Start the CNC milling machine and begin the machining operation. The CNC control system automatically controls the spindle and feed motion of the milling machine based on the pre-programmed machining program to achieve cutting of the workpiece.
f. Completion
Superity
Compared to manual milling machines, CNC milling machines offer higher efficiency, excellent precision, high flexibility, and stable quality control.
III. CNC lathe
Briefly Intro
CNC lathes are essential in Firearm Magazine Production due to their ability to produce highly precise and consistent cylindrical parts. These machines utilize computer numerical control technology to automate and control the turning processes, ensuring that each component meets stringent tolerance requirements.
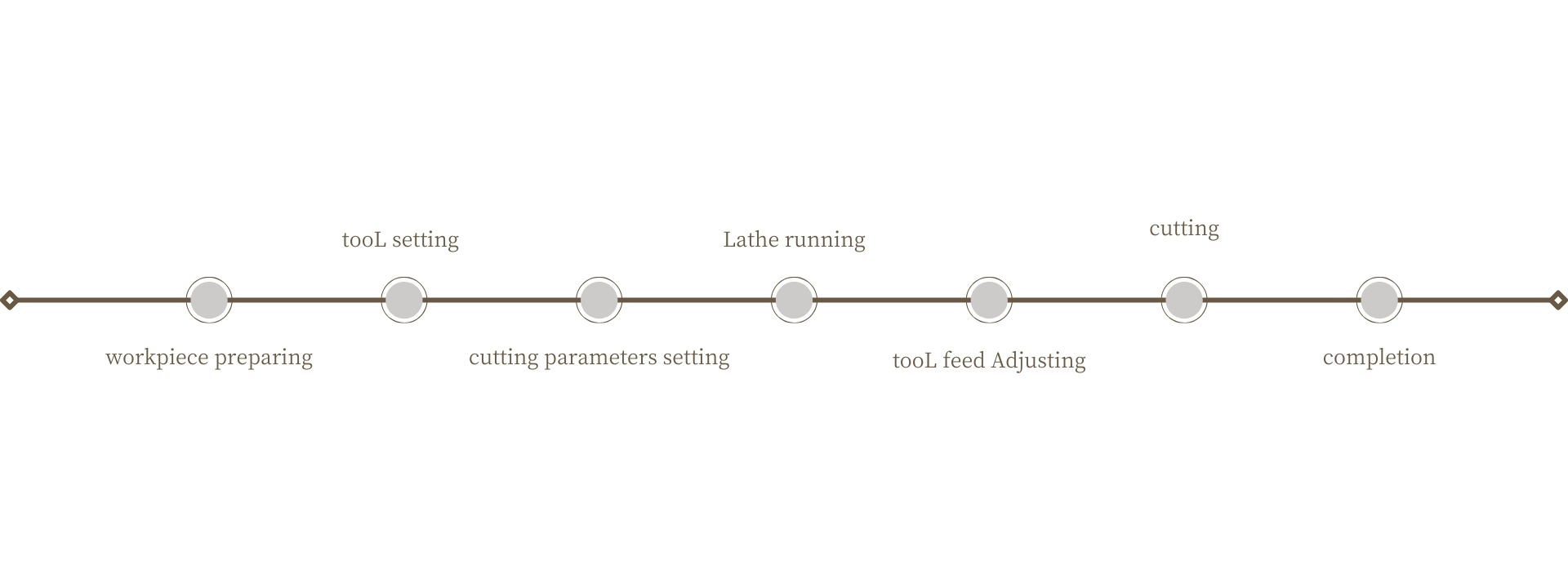
a. Workpiece Preparing
Mount the workpiece to be machined on the spindle of the lathe.
b. Tool Selecting
Choose the appropriate tool based on the material and shape of the workpiece.
c. Cutting parameters setting
Adjust the cutting parameters of the lathe, including tool speed, feed rate, and cutting depth.
d. Lathe Running
Turn on the power switch of the lathe to start it.
e. Tool feed Adjusting
Adjust the tool feed to move along the axis of the workpiece.
f. Cutting
The tool starts cutting the surface of the workpiece.
g. Completion
Perform inspection and measurement to ensure that the machining quality meets the requirements.
Superity
Compared to manual milling machines, CNC milling machines offer higher efficiency, excellent precision, high flexibility, and stable quality control.
IV. Stamping Press
Briefly Intro
Stamping presses are crucial in Firearm Magazine Production due to their ability to efficiently shape and form metal parts with high precision. These machines utilize powerful presses and dies to cut, shape, and form metal sheets into specific components, ensuring consistency and accuracy in mass production.
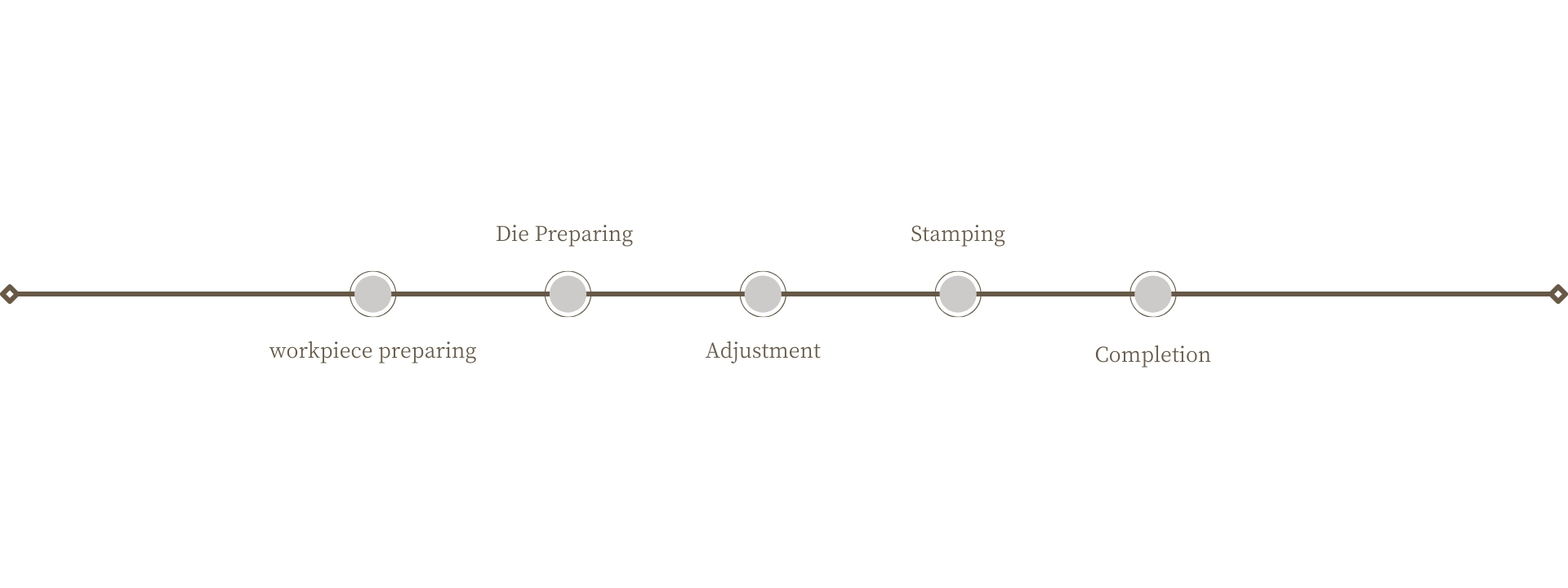
a. Workpiece Preparing
Place the metal sheet or strip to be processed on the worktable of the press.
b. Die Installing
Select the appropriate punch and die. The upper and lower parts of the die are respectively installed on the punch and the press.
c. Adjustment
Adjust the descent speed and process of the punch, as well as the position of the die.
d. Stamping
Apply high pressure to the workpiece when the punch contacts the die to form the desired shape
e. Completion
Superity
Stamping technology offers excellent precision and consistency, can process complex shapes, and can save material waste in the production process.
V. Metal Injection Molding(MIM)
Briefly Intro
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a cutting-edge technology used in Firearm Magazine Production to create complex and precise metal components. This process combines the versatility of plastic injection molding with the strength and durability of metal, allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality parts with intricate geometries.
a. Preparation
Metal materials are processed into powder form, ensuring uniform particle size and stable metal properties.
b. Injection molding
Metal powder is loaded into the hopper of a metal injection molding machine, heated to a high temperature, and pressure is applied to inject it into the mold cavity through the nozzle, filling the mold cavity.
c. Cooling
Allow the metal powder to cool and solidify in the mold.
d. Completion
After the metal powder is solidified and formed, open the mold to remove the finished product.
Superity
Metal injection molding can save materials, increase design flexibility, and offer a wider range of material choices during the production process.
VI.Heat Treatment
Briefly Intro
Heat treatment is a crucial process in Firearm Magazine Production, utilized to enhance the mechanical properties and performance of metal components. This process involves heating the metal parts to specific temperatures and then cooling them at controlled rates to achieve desired material properties.
VII.Surface Treatment
Briefly Intro
Surface treatment is integral to Firearm Magazine Production, serving to enhance the durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics of metal components. This process involves applying various coatings or finishes to the surface of firearm magazine parts to achieve desired properties and appearance.

Polishing
Improves the appearance and texture, reduces friction resistance, and makes operation smoother.
Nitriding
Commonly used on components such as gun barrels and bolts.
Coating
Common coatings include anodized coatings, ceramic coatings, and polymer coatings.
Electroplating
Common electroplating materials include nickel, chromium, or gold plating.
VIII.Welding
Briefly Intro
Welding plays a crucial role in Firearm Magazine Production, facilitating the assembly of various components to create durable and reliable firearm magazines. This process involves joining metal parts together by heating them to a melting point and then allowing them to cool, resulting in a strong bond.
IX.Forging
Briefly Intro
Forging is a critical process in Firearm Magazine Production, utilized to manufacture durable and reliable magazine components with high strength and precision. This process involves shaping metal by applying compressive forces through the use of dies and hammers
a. Preparation and Preheating
Select the appropriate metal material and cut or trim it to the desired shape and size. Preheat it to the appropriate temperature to increase its plasticity.
b. Mold Making and Installation
Create dedicated forging dies. Place the preheated metal material on the lower die and install the upper die to prepare for forging operation.
c. Forging
Apply pressure using forging machinery or manual forging tools to deform the metal material plastically in the mold. By continuously adjusting and applying pressure, gradually shape the metal material into the desired shape.
d. Completion
Superity
Forging is the best choice for strengths and durability. Alongside this, it provides precision of parts, enhances material performance, and saves materials and energy.
X.Casting
Briefly Intro
Casting is a fundamental process in Firearm Magazine Production, allowing for the efficient and cost-effective manufacture of various magazine components. This process involves pouring molten metal into a mold cavity, where it solidifies and takes the shape of the mold.
a. Mold Preparation
Create molds that meet the requirements of the product design.
b. Pre-processing
Select the appropriate metal material and heat it to its melting temperature, ensuring uniform temperature and fluidity of the metal.
c. Mold Preheating
Treat the prepared casting mold surface as needed to improve casting quality and surface smoothness.
d. Injection Casting
Inject the molten metal from the furnace into the preheated mold. Adjust the injection pressure and speed according to the product shape and mold design to ensure that the metal fills all the spaces in the mold.
e. Cooling
Allow the metal to cool and solidify in cooling water or other cooling media.
f. Completion
Superity
Casting is a metal processing process with high design freedom, which can produce cost-effective, wide material selection, high production efficiency, high material utilization, and good surface finish.
XI. Laser Engraving
Briefly Intro
Laser engraving is a valuable technique in Firearm Magazine Production, offering precise and customizable marking and identification solutions for magazine components. This process utilizes a focused laser beam to remove material from the surface of metal parts, creating permanent marks, logos, serial numbers, or other designs.
1.Firearm Parts Production
Laser engraving can be used to manufacture components such as barrels, bolts, receivers, and grips for firearms. These parts require high precision and durability, which laser engraving can achieve.
2.Marking and Identification
Laser engraving can be used to mark labels, serial numbers, and other identification information on military equipment. This is crucial for tracking and managing inventory of military equipment.
3.Anti-counterfeiting Markings
Laser engraving can create anti-counterfeiting markings to help ensure the authenticity and security of military equipment.
4.Armor Material Processing
Laser engraving can be used to process armor materials, improving the strength and durability of armor.
XII. Conclusion
In conclusion, Firearm Magazine Production encompasses a range of specialized techniques and processes that highlight the unique considerations and priorities within the firearms industry. Unlike conventional industrial production, Firearm Magazine Production places particular emphasis on:
Precision and Reliability
Every component of a firearm magazine must meet exacting standards for precision and reliability to ensure the safe and consistent operation of firearms. Techniques such as CNC machining, forging, and casting are employed to achieve tight tolerances and durable constructions.
Durability and Performance
Firearm magazines are subjected to demanding conditions and rigorous use, requiring components that can withstand high levels of stress, abrasion, and corrosion. Processes like heat treatment, surface treatment, and laser engraving enhance the durability, wear resistance, and longevity of magazine components.
Regulatory Compliance and Traceability
Firearm magazines must comply with various regulatory requirements and standards, necessitating meticulous documentation, marking, and identification of components. Laser engraving is utilized to ensure compliance with regulations and facilitate traceability throughout the manufacturing and distribution process.
Customization and Branding
Firearms enthusiasts often seek customization options and personalized touches for their firearms and accessories. Laser engraving allows for the customization of magazine components with unique designs, logos, or markings, catering to individual preferences and enhancing brand identity.
Safety and Quality Control
The safety and quality of firearm magazines are paramount concerns, necessitating stringent quality control measures and testing protocols. Advanced inspection techniques, such as non-destructive testing and dimensional analysis, are employed to ensure that magazine components meet the highest standards of safety and performance.